Analyzing Initial Access Across Today's Business Environment
Initial access represents a critical focus area for security practitioners. The Huntress Tactical Response and Security Operations Center (SOC) teams analyzed intrusion data to identify the most prevalent attack vectors organizations face today.
About Tactical Response
The Huntress Tactical Response team serves as an escalation point for complex, multi-host intrusions. These analysts identify initial access vectors by examining Windows events and requesting additional telemetry from partners, including logs from edge devices. Their goal is to help organizations rapidly understand breach sources and implement corrective measures.
Key Findings on Initial Access Methods
Analysis of completed engagements reveals a clear pattern in how attackers gain network access:
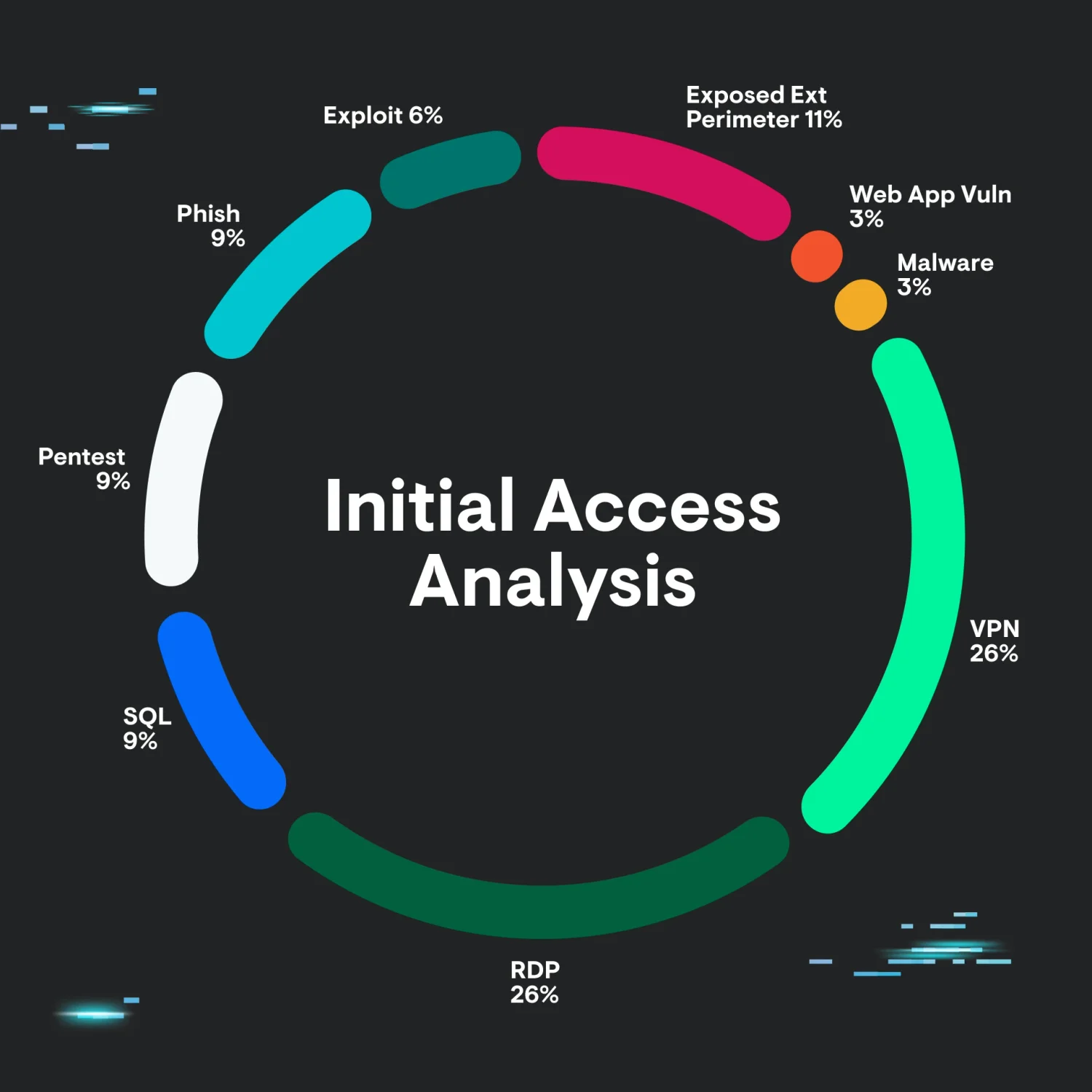
Top Initial Access Vectors:
- Remote Desktop (RDP)
- Virtual Private Networks (VPN)
- Exposed external perimeter
- Other methods (exploitation, phishing, etc.)
The research shows that “basic tradecraft” approaches significantly outnumber sophisticated techniques. As the analysis notes: “threat actors are finding success via tried and true methods of exploitation.”
RDP and Exposed Perimeter Vulnerabilities
Common Attack Patterns
Attackers frequently employ brute-force attempts followed by successful logins. In other cases, credentials appear compromised previously and reused in credential stuffing attacks. Remote Desktop Gateway (RDG) services face similar threats with slightly different telemetry signatures.
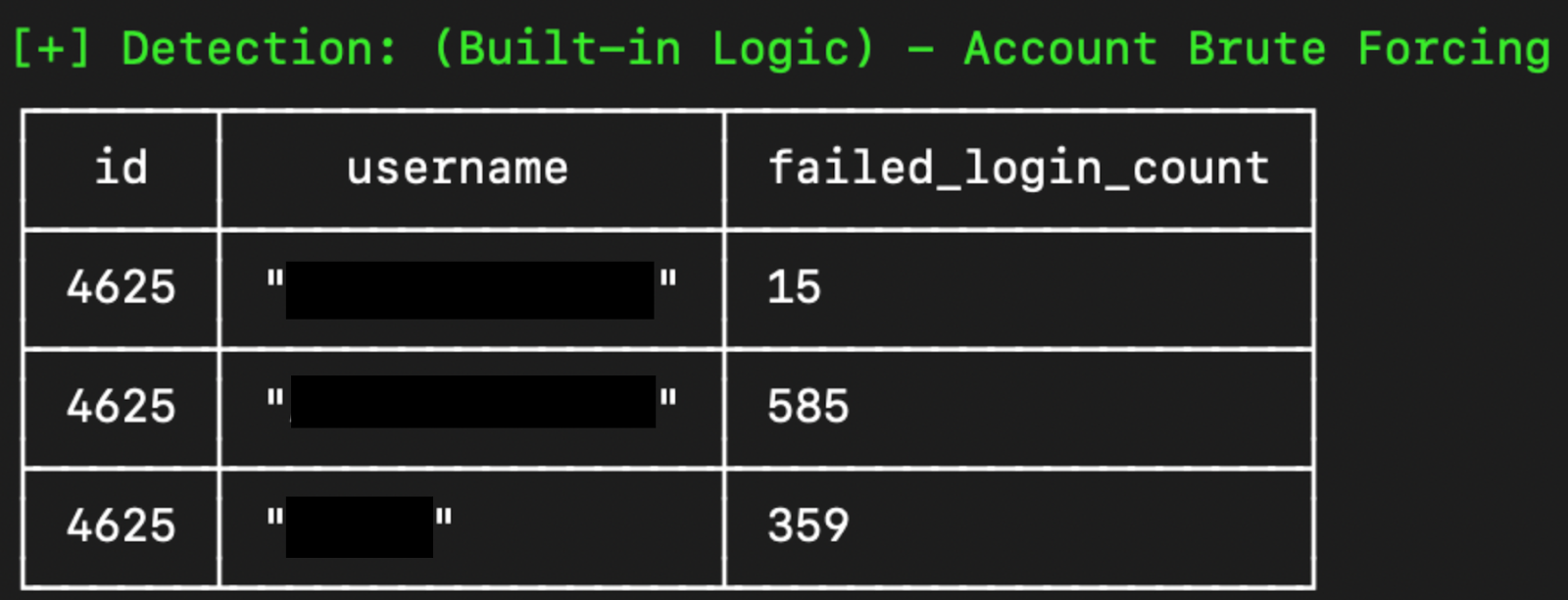
Critical Risk: Exposed SMB
Server Message Block (SMB) exposure represents extreme danger—the protocol lacks multi-factor authentication support entirely. Valid credentials alone enable network access.
Security Recommendations
For RDP/RDG/SMB Protection:
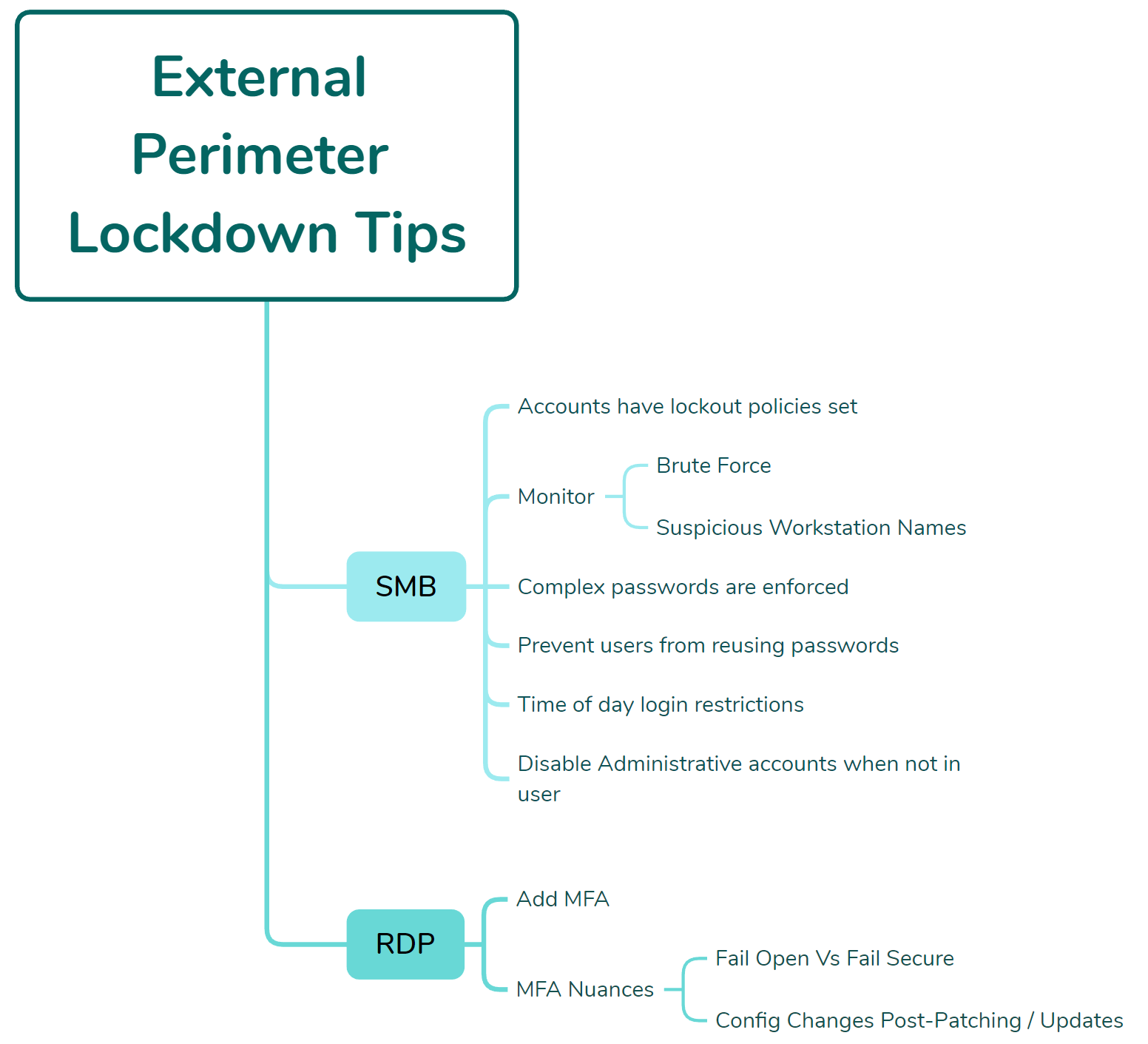
- Enforce account lockout policies
- Monitor for brute-force attack patterns
- Implement complex password requirements
- Prevent password reuse across accounts
- Add time-of-day login restrictions
- Disable unused administrative accounts
- Test authentication flows after patches and updates
MFA Implementation Cautions:
Organizations should be aware of “fail open” configurations where MFA bypasses occur if applications crash. Additionally, patching cycles can inadvertently modify or disable MFA settings—authentication workflows require post-update testing.
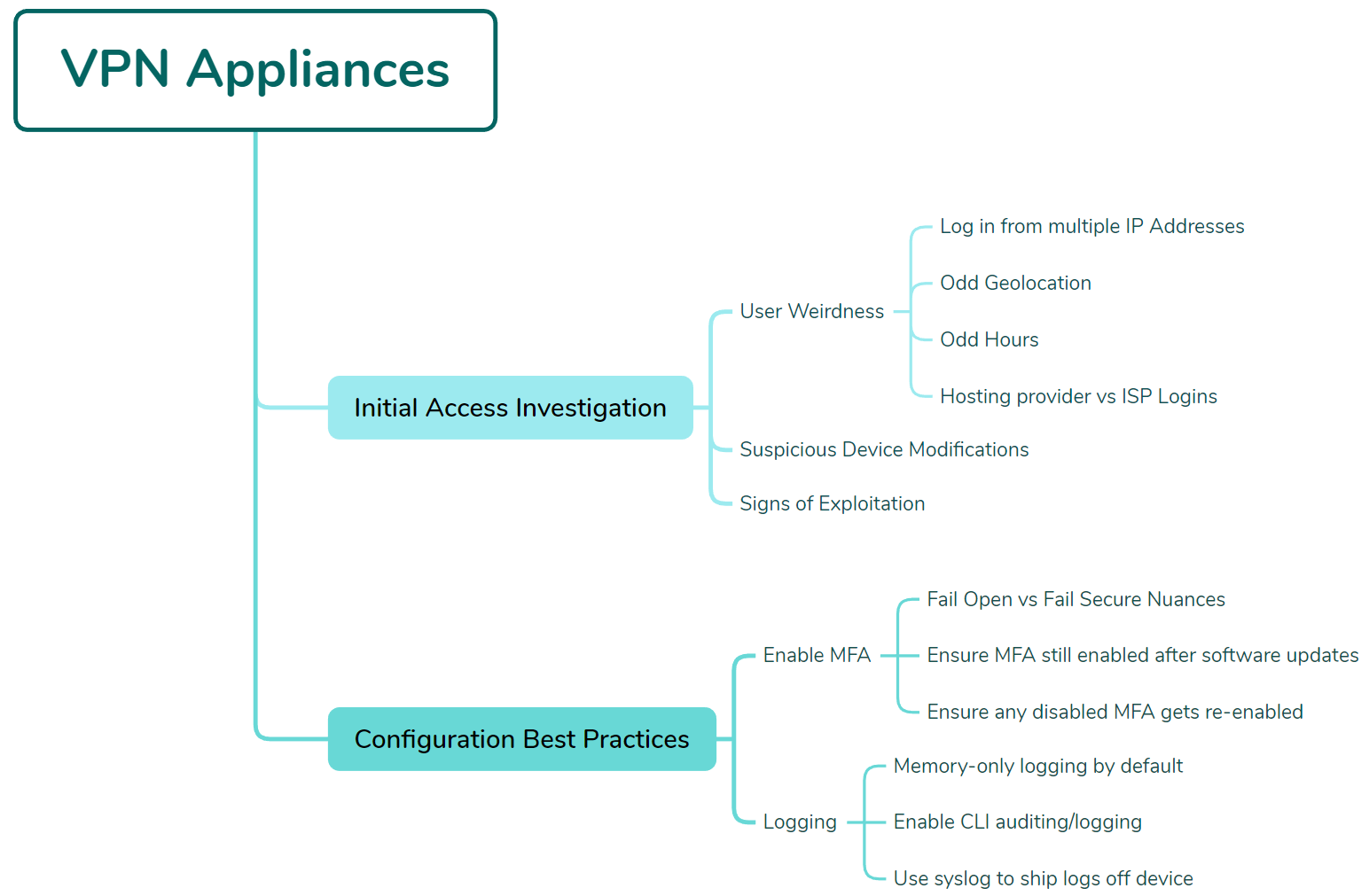
VPN Appliance Security
Configuration Best Practices
VPN devices demand robust logging configuration since they face constant internet scanning and probing. Key investigation focuses include:
- Multiple IP address logins from single users
- Suspicious geolocation access patterns
- Unusual login timing
- Configuration modifications to appliance settings
- Hosting provider access (versus residential ISPs)
Fortinet Example Configuration
Enable CLI audit logging:
config system global
set cli-audit-log enable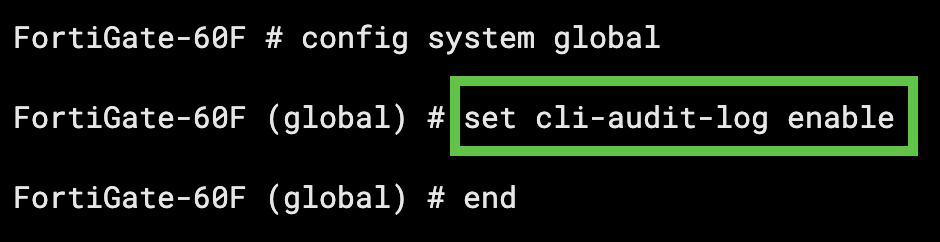
Configure syslog forwarding for log preservation:
config log syslogd setting
set status enable
set server <syslog_server_ip>
set format { default | cev | cef }
This approach preserves log integrity while enabling centralized analysis.
Strategic Takeaway
Despite industry focus on zero-days and sophisticated attacks, organizations remain vulnerable to fundamental security gaps. The research demonstrates that “organizations…may not be doing the basics as well as we would like or hope for.” Defenders must prioritize securing exposed perimeters and enforcing strong authentication controls before addressing advanced threats.